In addition to being tremendously useful, some of the new features in XMLSpy 2009 are just plain cool. The complete list of new functionality includes:
- Support for XBRL 2.1 and XBRL Dimensions 1.0
- XBRL Taxonomy Editor
- XPath auto-completion
- Native support for additional databases
- Support for XML fields in SQL Server
- Extensions for identity constraints editing in Schema View
- Expanded source control system support
- Support for the XSLT extension altova:evaluate
- Support for Apache FOP 0.95
We’ve already blogged quite a bit about the first two items on the list: support for XBRL validation and XBRL taxonomy editing. Some more details on the other new features are below.
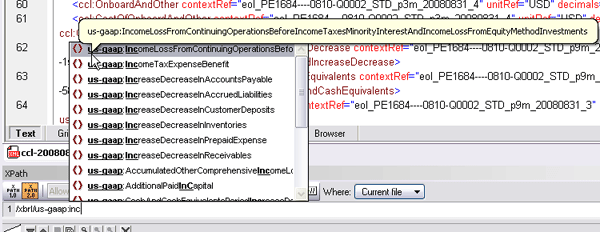
Intelligent XPath Auto-Completion
We’ve been delighted to receive feedback from customers who are really excited about this new feature. If you’re developing XSLT or XQuery, writing XPath expressions just got a lot easier. As you’re composing an XPath expression in Text View, Grid View, or the XPath Analyzer, XMLSpy now provides you with valid XPath functions, as well as element and attribute names from the associated schema and XML instance(s). XMLSpy’s intelligent XPath auto-completion accounts for namespaces when listing options and even provides deep path suggestions when the required node is not in close proximity to the current context. 
Native Support for Additional Databases
XMLSpy 2009 adds new native support for the latest versions of SQL Server and Oracle, and brand new support for PostgreSQL. Support for DBs in XMLSpy allows you to generate an XML Schema based on a database, import and export data based on database structures, and generate relational database structures from XML Schemas, and so on. The built-in Database Query window lets you perform queries against the database and edit the data. Here’s the complete list of databases with native support in XMLSpy:
- Microsoft® SQL Server® 2000, 2005, 2008
- IBM DB2® 8, 9
- IBM DB2 for iSeries® v5.4
- IBM DB2 for zSeries® 8, 9
- Oracle® 9i, 10g, 11g
- Sybase® 12
- MySQL® 4, 5
- PostgreSQL 8
- Microsoft Access™ 2003, 2007
SQL Server support has also been enhanced to allow viewing and editing of XML fields that are stored in the database.
Extensions for Identity Constraint Editing in Schema View
Configuring identity constraints (i.e., key/keyref/unique values) is an important aspect of XML Schema development, especially for database users. Adding to existing support for editing these identity constraints, there are now enhanced visual cues and editing options in XMLSpy 2009. A new tab Identity Constraints tab in the Components entry helper window displays all existing constraints in a tree view and allows you to easily modify or create new relationships. Furthermore, identity constraints are now indicated by green lines, informative icons, and mouse-over messages in the Content Model View. A right-click menu allows you to easily add new relationships and specify field and selector values by typing them manually, using drop-down entry helpers, or by simply dragging and dropping the desired nodes. 
Expanded Source Control System Support
Based on customer feedback, we’ve completely reworked the source control system interface in XMLSpy and also added the same level of source control support to UModel, our UML modeling tool, allowing both products to intelligently integrate with all major SCM tools. Once a project is bound to a version control system, XMLSpy automatically monitors the status of all files and prompts the you to check out a file whenever you starts to modify the document. In addition, the actual state of each file is shown through checkmarks or locks in the upper right corner of each file icon. What do you think of these new features? What would you like to see added to the next version of XMLSpy? Let us know by commenting below.




















 Let’s take a look at how we created this XSLT code.
Let’s take a look at how we created this XSLT code.





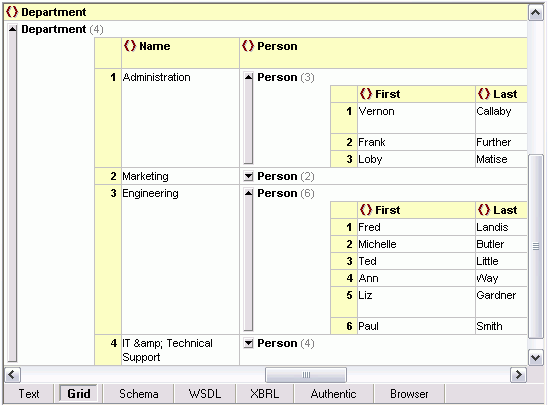 Of course let’s not forget that the XMLSpy
Of course let’s not forget that the XMLSpy